Hull Moving Average (HMA)
Alan Hull developed Hull Moving Average in 2005 in his quest to create a moving average that is "responsive to current price activity while maintaining curve smoothness". Hull claims that his moving average "almost eliminates lag altogether and manages to improve smoothing at the same time".
Hull Moving Average Trading Signals
Alan Hull recommends using his moving average for directional signals and not for crossovers which could be distorted by the lag.
- Go long when HMA turns up; and
- Go short when HMA turns down.
It would make sense to introduce a longer-term moving average to signal trend direction, then only take trades in the direction of the trend.
Example
The weekly chart of CSL Ltd (CSL) compares the 13-week Hull Moving Average to a 13-week Simple Moving Average.
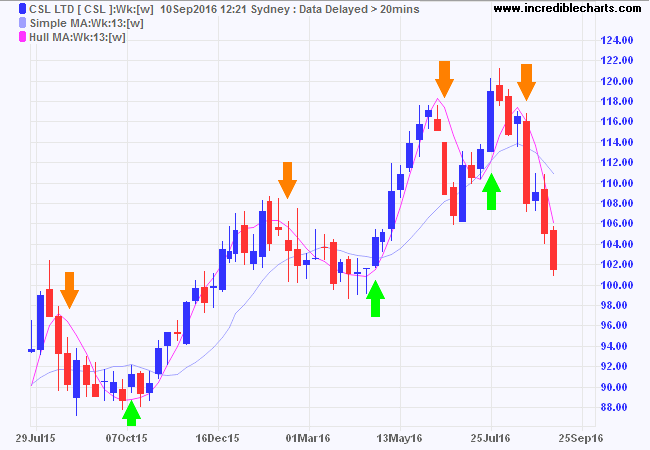
Note that signals are taken at the end of the weeks flagged, not the beginning.
Two HMA Example
We again use the weekly chart of CSL Ltd (CSL), this time with 13-week and 52-week Hull Moving Averages.
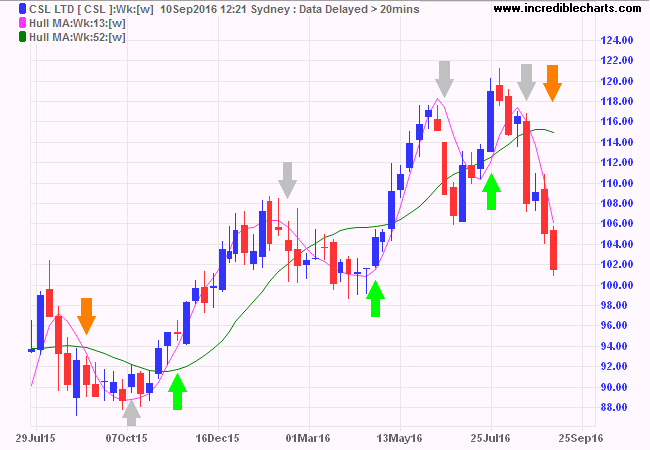
Trend direction is taken from the green 52-week Hull Moving Average. Trade signals are taken from the faster 13-week Hull Moving Average but only when the 52-week MA slopes in the same direction.
- Green = go Long
- Orange = go Short
- Gray = Exit trade
Setup
Hull uses a 16-week moving average in his examples. I would have thought that 13 weeks (quarter of a year) would make more sense and be more defensible against accusations of curve-fitting (retrospectively fitting an indicator to the data).
Select Indicators and Moving Averages in the left column of the Indicator Panel. Select Hull from the drop-down box of moving average types.
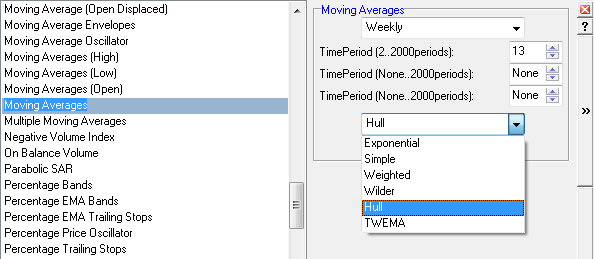
To alter the settings, see Edit Indicator Settings.
Colors
To amend indicator colors, open the legend by clicking "L" on the toolbar or typing "L" on your keyboard. Adjust individual colors by clicking on the color patches next to the indicator in the legend.
Hull Moving Average Formula
Alan Hull uses three Weighted Moving Averages (WMA) in his formula:
Calculate the WMA for the Period (e.g. 13 Weeks).
Divide the Period by 2 and use the Integer value to calculate a second WMA.
Multiply the second WMA by 2 then subtract the first WMA.
Calculate the Square Root of the Period and take the Integer value.
Use the resulting Integer value to calculate a third WMA of the result from the first two WMAs.
Notation
Here is more mathematical notation for n periods:
WMA(Integer(SQRT(n)),WMA(2*Integer(n/2),data) - WMA(n,data))

Author: Colin Twiggs is a former investment banker with almost 40 years of experience in financial markets. He co-founded Incredible Charts and writes the popular Trading Diary and Patient Investor newsletters.
Using a top-down approach, Colin identifies key macro trends in the global economy before evaluating selected opportunities using a combination of fundamental and technical analysis.
Focusing on interest rates and financial market liquidity as primary drivers of the economic cycle, he warned of the 2008/2009 and 2020 bear markets well ahead of actual events.
He founded PVT Capital (AFSL No. 546090) in May 2023, which offers investment strategy and advice to wholesale clients.
